Watch: GDA2020 & Dynamic Datums
Do you work with spatial information? Are you aware of the shift to GDA2020? Here’s what you need to know about GDA2020.
The Big Shift to GDA2020
Australia is currently transitioning to a new national geodetic datum, moving from GDA94 to the new Geocentric Datum of Australia 2020 (GDA2020). This transition will significantly impact the architectural, engineering and construction industries, which rely on millimetre-accurate spatial information. GDA2020 will bring Australia’s spatial information in-line with global satellite positioning systems (GNSSs).
Isn’t Global Standardisation a Good Thing?
Eventually, yes. But initially this will mean that Australian spatial information will move by 1.8m, potentially making coordinates inaccurate and unusable unless the specific datum is defined (GDA94 or GDA2020).
What Is a National Geodetic Datum?
A geodetic datum is a positioning system that enables coordinates to identify a specific location on the Earth’s surface. They’re the fundamental positioning system for any country.
GDA94 and GDA 2020 are plate-fixed geocentric datums, which use reference points that are static to the Earth’s tectonic plates. Therefore, they appear to be unchanging or ‘static’ over time as they move with tectonic movements.
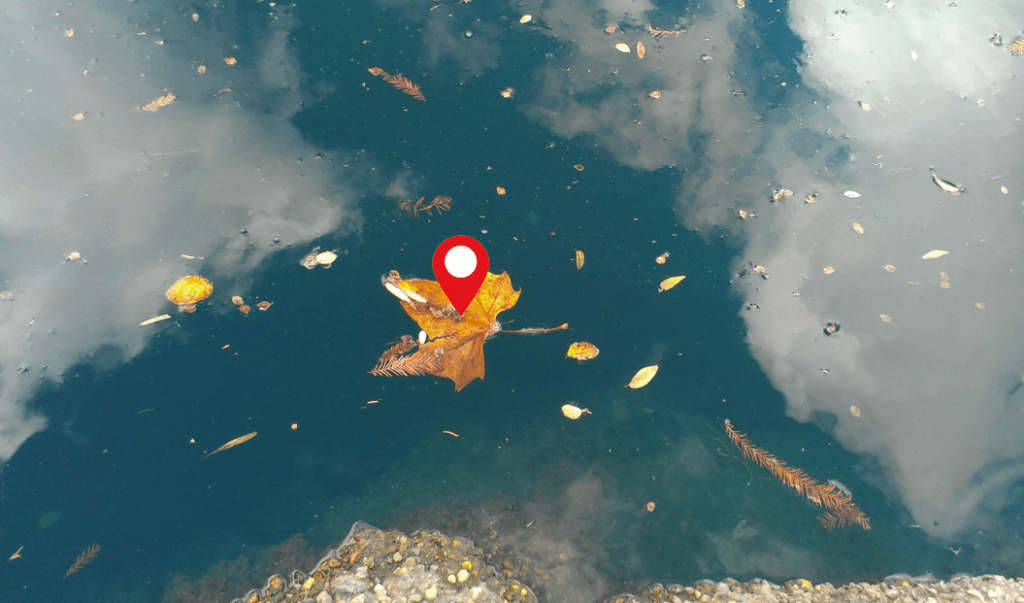

To explain this, imagine a leaf with a red dot on it floating in a pond. Ripples on the water’s surface will move the leaf and the red dot. However, in regards to the leaf itself, the red dot hasn’t moved at all. This is how plate-fixed geocentric datums operate.
The Problem With Plate-Fixed Geocentric Datums
The problem is that the Earth’s tectonic plates are not static. Like that leaf drifting on your hypothetical pond, every continent is floating on a sea of molten rock. You can’t feel it, but the Earth’s tectonic plates are constantly moving in different directions at different speeds.
The Australian tectonic plate is one of the fastest moving plates, drifting in a north-easterly direction at a rate of approximately 7cm per year – or about the same rate as your fingernail grows. As our plates move, plate-fixed spatial information becomes less accurate. Since GDA94’s inception on the 1st January 1994, the Australian continent has moved about 1.8 metres, and this gap continues to widen.
‘Earth-Fixed’ ITRF Satellite Location Technology
GNSSs use the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) to determine location. These datums are ‘earth-fixed’: the coordinates of reference points are defined against the whole solid Earth, not a tectonic plate. This means that ITRF datums appear to change over time with tectonic movement. This creates a problem…
The Disparity Between GDA and ITRF
When GDA94 was implemented, GNSS technology, such as GPS, was only accurate to 100m. So tectonic movement of several centimetres was relatively unimpactful. However, the emergence of new metre-accurate GNSS technology means that Australia’s GDA94 coordinates are no longer aligned with ITRF. There is now a 1.8m disparity between GDA and ITRF coordinates because GDA94 does not factor in tectonic movement.
This can cause serious implications for applications that rely on accurate satellite positioning, such as surveying and civil engineering, automated mining operations and precision agriculture.
GDA2020: Modernising Australia’s Datum
To address this issue, Australia is transitioning its datum to where the Australian tectonic plate will be on the 1st of January 2020 (GDA2020). GDA2020 uses the same ellipsoid as GDA94 but uses a different epoch. An epoch is the latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates captured at a fixed point in time. That means locations under GDA2020 will be defined 1.8m north-east of where they were previously under GDA94. Over the next few years, GPS locations will converge with the location of GDA2020.

What Does GDA2020 Mean to the AEC Industry?
In short: know your data, know your datum, know your epoch. If you want to be precise, everything has to be defined!
Going From GDA94 to GDA2020 in 12d
12d Model 14 provides two methods for converting your spatial data from GDA94 to GDA2020: 7 Parameter Similarity Transformation and NTV2 Grid.
To learn more about the specific steps YOU need to take, we have a free video presented by 12d Solutions Managing Director Dr lee Gregory. The video will cover:
- The evolving model of the earth
- GDA2020
- Dynamic Datums
- AEC best practices

Author